The Anti-Microbial Resistance Research Hub supports stronger coordination, knowledge sharing and faster progress in AMR research across the Globe. This is an open and free resource for a global community of practice for all researchers, healthcare and laboratory teams working in all organisations working in AMR research.
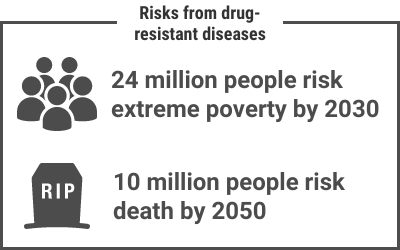 The UN’s Interagency Coordinating Group on AMR stated in 2019, drug-resistant diseases could force up to 24 million people into extreme poverty by 2030 and cause 10 million deaths each year by 2050. Its financial impact would be on a scale similar to the 2008 financial crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic. The AMR Research Hub will share current advances and best practices in AMR and raise research visibility, opportunities and engagement for public health providers, policy makers and the entire research community in all sectors to actively participate in generating new evidence to tackle AMR.
The UN’s Interagency Coordinating Group on AMR stated in 2019, drug-resistant diseases could force up to 24 million people into extreme poverty by 2030 and cause 10 million deaths each year by 2050. Its financial impact would be on a scale similar to the 2008 financial crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic. The AMR Research Hub will share current advances and best practices in AMR and raise research visibility, opportunities and engagement for public health providers, policy makers and the entire research community in all sectors to actively participate in generating new evidence to tackle AMR.
The Global Health Network wishes to work with other organisations and global initiatives and collaborate to enable more and better research, identify the key priorities to combat anti-microbial resistance, agree common strategic research priorities and share protocols, standards and practices to address everyone’s aim to mitigate and eventually eliminate the threat of antimicrobial resistance.
This Research Hubs is coordinated by a working group from across partner organisations in Africa, Asia and Latin America. New partners from all types of organisations who have the shared aim of enabling more and better AMR research by supporting teams in places where such evidence and skills are lacking and to improve output and processes by sharing methods, data, tools and resources between all areas, roles, settings and contexts of AMR research are welcome.
The AMR Hub is partially funded by Pfizer Inc, who kindly provided sponsorship towards the design and initiation of the Hub. The balance of costs are met by the Global Health Network utilising existing resources.